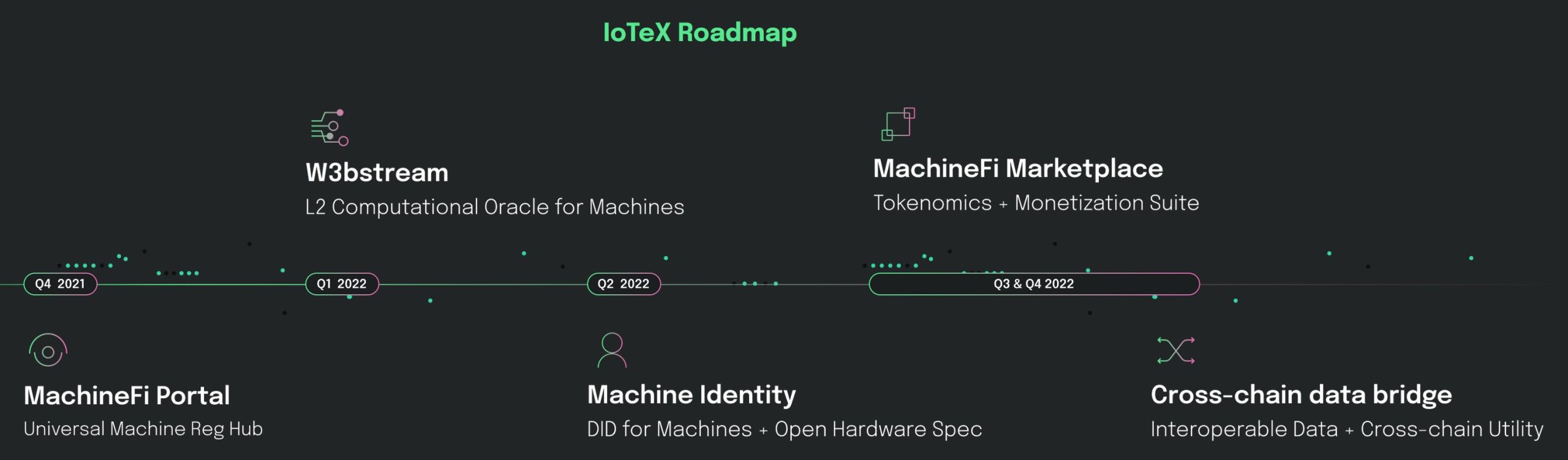
If you set up 2-Step Verification, you can use the Google Authenticator app to receive codes. You can still receive codes without internet connection or mobile service. Learn more about 2-Step Verification.
1- Android
App requirements
To use Google Authenticator on your Android device, you need:
- Android version 4.4 or up
- 2-Step Verification turned on
Download Authenticator
Set up Authenticator
- On your Android device, go to your Google Account.
- At the top, tap the Security tab.
If at first you don’t get the Security tab, swipe through all tabs until you find it. - Under “Signing in to Google,” tap 2-Step Verification. You may need to sign in.
- Under “Authenticator app,” tap Set up.
On some devices, under “Authenticator app,” tap Get Started. - Follow the on-screen steps.
Get codes on new phone
Transfer Google Authenticator codes to new phone
To transfer Authenticator codes to a new phone, you need:
- Your old Android phone with Google Authenticator codes
- The latest version of the Google Authenticator app installed on your old phone
- Your new phone
- On your new phone, install the Google Authenticator app.
- In the Google Authenticator app, tap Get Started.
- At the bottom, tap Import existing accounts?
- On your old phone, create a QR code:
- In the Authenticator app, tap More
Transfer accounts
Export accounts.
- Select the accounts you want to transfer to your new phone. Then, tap Next. If you transfer more than one account, your old phone may create more than one QR code.
- In the Authenticator app, tap More
- On your new phone, tap Scan QR code.
After you scan your QR codes, you get confirmation that your Authenticator accounts transferred.
Tip: If your camera can’t scan the QR code, there may be too much information. Try to export again with fewer accounts.
Change which phone to send Authenticator codes
- On your Android device, go to your Google Account.
- At the top, tap Security.
- Under “Signing in to Google,” tap 2-Step Verification. You may need to sign in.
- Under “Available second steps,” find “Authenticator app” and tap Change Phone.
- Follow the on-screen steps.
Common issues
Fix an incorrect code
If your code is incorrect, confirm:
- You entered the code before it expired.
- The time on your device is correct for your local time zone.
If your code is still incorrect, sync your Android device:
- On your Android device, open the Google Authenticator app
.
- In the top right, select More
Time correction for codes
Sync now.
- On the next screen, the app confirms the time is synced. You can use your verification codes to sign in.
- The sync only affects the internal time of your Google Authenticator app. Your device’s Date & Time settings won’t change.
Use Authenticator on multiple accounts or devices
Set up 2-Step Verification for multiple accounts
Authenticator can issue codes for multiple accounts from the same mobile device. Each Google Account must have a different secret key.
To set up extra accounts:
- Turn on 2-Step Verification for each account. Learn more about 2-Step Verification.
- Use the same Authenticator app for each account.
Set up Google Authenticator on multiple devices
To get verification codes on more than one device:
- On the devices you want to use, make sure you install Authenticator.
- In your Google Account, go to the 2-Step Verification section.
- If you already have Authenticator for your account, remove that account from Authenticator.
Important: Before you remove an account from Authenticator, make sure you have a backup. Learn more about backup codes.
- To set up 2-Step Verification for the Authenticator app, follow the steps on screen. Use the same QR code or secret key on each of your devices. Learn more about 2-Step Verification.
- To check that the code or key works, make sure the verification codes on every device are the same.
2- iPhone & iPad (iOS)
App requirements
To use Google Authenticator on your iPhone, iPod Touch, or iPad, you need:
- The latest operating system for your device
- 2-Step Verification turned on
Tip: If you have an iPhone 3G or up, to use Authenticator, you can scan a QR code.
Download Authenticator
Set up Authenticator
- On your iPhone or iPad, go to your Google Account.
- At the top, tap Security.
- Under “Signing in to Google,” tap 2-Step Verification. You may need to sign in.
- Under “Add more second steps to verify it’s you,” find “Authenticator app” and tap Set up.
- Follow the on-screen steps.
Get Google Authenticator codes on a new phone
Transfer Authenticator codes to a new phone
You need:
- Your old iPhone with Authenticator codes
- The latest version of the Google Authenticator app installed on your old phone
- Your new phone
- On your new phone, install the Google Authenticator app.
- In the app, tap Get Started.
- At the bottom, tap Import existing accounts?.
- On your old iPhone, create a QR code:
- In the Authenticator app, tap More Export accounts Continue.
- Select the accounts you want to transfer to your new phone, then tap Export.
- If you transfer multiple accounts, your old phone may create more than one QR code.
- On your new phone, tap Scan QR code.
- After you scan your QR codes, you get a confirmation that your Google Authenticator accounts transferred. You can remove your exported accounts from your old phone.
Tip: If your camera can’t scan the QR code, it may be that there’s too much info. Try to export again with fewer accounts.
Change which phone to send Authenticator codes
- On your Android device, go to your Google Account.
- At the top, tap Security.
- Under “Signing in to Google,” tap 2-Step Verification. You may need to sign in.
- Under “Available second steps,” find “Authenticator app” and tap Change Phone.
- Follow the on-screen steps.
Use Authenticator on multiple accounts or devices
Set up 2-Step Verification for multiple accounts
Authenticator can issue codes for multiple accounts from the same mobile device. Each Google Account must have a different secret key.
To set up extra accounts:
- Turn on 2-Step Verification for each account. Learn more about 2-Step Verification.
- Use the same Authenticator app for each account.
Set up Google Authenticator on multiple devices
To get verification codes on more than one device:
- On the devices you want to use, make sure you install Authenticator.
- In your Google Account, go to the 2-Step Verification section.
- If you already have Authenticator for your account, remove that account from Authenticator.
Important: Before you remove an account from Authenticator, make sure you have a backup. Learn more about backup codes.
- To set up 2-Step Verification for the Authenticator app, follow the steps on screen. Use the same QR code or secret key on each of your devices. Learn more about 2-Step Verification.
- To check that the code or key works, make sure the verification codes on every device are the same.